|
|||||
| 1. | a. | cosα = (-1 • -4 + 5 • -7)/(√26 • √65) = -31/41,11 = -0,754 ⇒ α = 138,9º of 41,1º | |||
| b. | cosα = (0 • 6 + 4 • -4)/(√16 • √52) = -16/28,84 = -0,555 ⇒ α = 123,7º of 56,3º | ||||
| c. |
 |
||||
| cosα = (1 • -4 + 2 • 3)/(√5 • √25) = 2/11,18 = 0,179 ⇒ α = 76,7º | |||||
| d. |
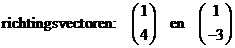 |
||||
| cosα = (1 • 1 + 4 • -3)/(√17 • √10) = -11/13,04 = -0,844 ⇒ α = 147,5º of 32,5º | |||||
| e. |
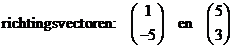 |
||||
| cosα = (1 • 5 + -5 • 3)/(√26 • √34) = -10/29,73 = -0,336 ⇒ α = 109,7º of 70,3º | |||||
| 2. | cosα
= (-3 • 1 + a • 2)/(√5
• √(a²
+ 9)) = ±1/2√3 -3 + 2a = ±1/2√3 • √(a2 + 9) • √5 -6 + 4a = ±√15 • √(a2 + 9) 36 - 48a + 16a2 = 15a2 + 135 a2 - 48a - 99 = 0 a = (48 ± √2700)/2 = (48 ± 30√3)/2 = 24 ± 15√3 (ongeveer -1,98 en 49,98) |
||||
| 3. | a. |
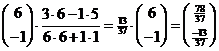 |
|||
| b. |
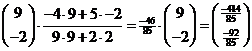 |
||||
| 4. | Bereken de projectie van OP op de richtingsvector van de lijn (dat is 2 opzij, 7 omhoog): | ||||
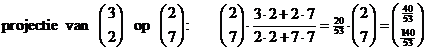 |
|||||
| De projectie is het punt P' = (40/53, 140/53) | |||||
| 5. |
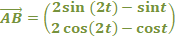 |
||||
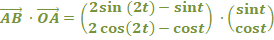 |
|||||
| bij
een hoek van 90º moet dat nul zijn: (2sin(2t) - sint) • sint + (2cos(2t) - cost) • cost = 0 2sin(2t)sint - sin2t + 2cos(2t)cost - cos2t = 0 omdat sin2t + cos2t = 1 geeft dat: 2sin(2t)sint + 2cos(2t)cost = 1 sin(2t)sint + cos(2t)cost = 1/2 Maar die linkerkant is precies gelijk aan cos(2t - t) cos(2t - t) = 1/2 cost = 1/2 t = 1/3π + k2π ∨ x = -1/3π + k2π Op dit interval geeft dat t = 1/3π |
|||||
| 6. | Stel P = (0, p) | ||||
|
|
|||||
| Die staan loodrecht op elkaar als het inproduct
nul is: -2 • 6 + (3 - p)•(7 - p) = 0 -12 + 21 - 3p - 7p + p2 = 0 p2 - 10p + 9 = 0 (p - 9)(p - 1) = 0 p = 9 ∨ p = 1 Dat zijn dus de punten (0, 1) en (0, 9) |
|||||
| 7. | P
= (0, 1/p) Q = (π, -1/p) R = (2π, 1/p) |
||||
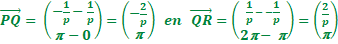 |
|||||
| Voor
loodrechte stand moet het inproduct nul zijn: -2/p • 2/p + π • π = 0 -4/p² + π2 = 0 4/p² = π2 p2 = 4/π² p = 2/π ∨ p = -2/π |
|||||
| 8. | a. | Kies
een assenstelsel met de oorsprong in A AF is de lijn y = 0,5x HD is de lijn y = 1 - 1/3x snijpunt: 0,5x = 1 - 1/3x 5/6x = 1 x = 6/5 dan is y = 3/5 AS is inderdaad de gevraagde vector, |
|||
| b. |
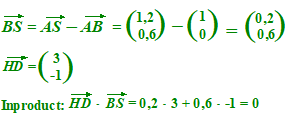 |
||||
| Het inproduct is NUL dus de vectoren staan loodrecht op elkaar. | |||||
| 9. | a. | De cosinussen van de hoeken tussen de richtingsvectoren moeten gelijk zijn. | |||
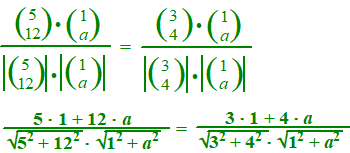 |
|||||
| Kruislings vermenigvuldigen: (5 + 12a) • 5 • √(1 + a2) = (3 + 4a) • 13 • √(1 + a2) 25 + 60a = 39 + 52a 8a = 14 a = 14/8 = 13/4 |
|||||
| b. | Lijn
m moet door het punt S gaan. Voor S geldt: 29 + 5s = 3t en 4 + 12s = 24 + 4t de tweede geeft t = -5 + 3s en dat kun je invullen in de eerste: 29 + 5s = 3(-5 + 3s) 29 + 5s = -15 + 9s 44 = 4s s = 11 Dan is S = (29 + 55, 4 + 132) = (84, 136) Als dat op lijn m ligt moet gelden: u = 84 en b + u • a = 136 b + 84 • 13/4 = 136 b = -11 |
||||
|
© h.hofstede (h.hofstede@hogeland.nl) |
|||||