|
|||||
| 1. | x = 10/(3
+ 2cost) 3 + 2cost = 10/x 2cost = 10/x - 3 cost = 5/x - 1,5 cos2t = (5/x + 1,5)2 sin2t = 1 - (5/x + 1,5)2 y = 4sin2t = 2 - 4(5/x + 1,5)2 cost ligt tussen -1 en 1 dan ligt x = 10/(3 + 2cost) tussen 2 en 10 dus het domein is [2, 10] |
||||
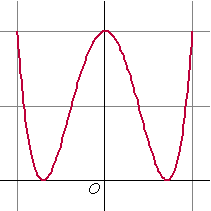
| 2. | a. |
 |
|||
| b. | y = 1 + cos 4t = 1 + 2cos2(2t) - 1 = 2cos2(2t) = 2(2cos2t - 1)2 = 2(4cos4t - 4cos2t + 1) = 8cos4t - 8cos2t + 2 = 8x4 - 8x2 + 2 |
||||
| 3. | a. | sint
• cost = 1/4 1/2sin2t = 1/4 sin2t = 1/2 2t = 1/6π + k2π ∨ 2t = 5/6π + k2π t = 1/12π + kπ ∨ t = 5/12π + kπ in het interval [0, 2π〉 geeft dat de oplossingen: t = 1/12π , 5/12π, 13/12π, 17/12π |
|||
| b. | y2
(?=?) x2(1 - x2) sin2tcos2t (?=?) cos2t • (1 - cos2t) (1 - cos2t) • cos2t (?=?) cos2t • (1 - cos2t) qed. |
||||
| 4. | a. | Voor
punt A geldt x = 0 dus 1 - t2
= 0 Dat geeft t = 1 ∨ t = -1 t = -1 geeft punt (0, 0) dus dat is niet A. Bij A hoort dus t = 1. x' = -2t dus voor t = 1 is x' = vx = -2 y' = 2(1 + t) dus voor t = 1 is y' = vy = 4 v = √(vy2 + vx2) = √((-2)2 + 42) = √20 = 2√5 |
|||
| b. | (x
+ y)2 = (1 - t2 + (1 + t)2)2 = (1 - t2 + 1 + 2t + t2)2 = (2 + 2t)2 = 4 + 8t + 4t2 = 4(t2 + 2t + 1) = 4(t + 1)2 = 4y qed. |
||||
|
© h.hofstede (h.hofstede@hogeland.nl) |
|||||