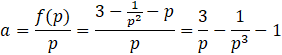|
|||||
| 1. | a. | de breedte is 4 - 2p de hoogte is 4p - p2 (het is de y die bij x = p hoort) oppervlakte = (4 - 2p)(4p - p2) = 16p - 4p2 - 8p2 + 2p3 = 16p - 12p2 + 2p3 |
|||
| b. | O ' = 16 - 24p
+ 6p2 = 0 ABC-formule: p = (24 ±√(576 - 384))/12 = 3,15 of 0,84 De gezochte oplossing is p = 0,84 O = 16p - 12p2 + 2p3 = 6,16 |
||||
| c. | De omtrek is 2(4 - 2p)
+ 2(4p - p2) = 8 - 4p + 8p - 2p2
= 8 + 4p - 2p2 afgeleide is nul: 4 - 4p = 0 p = 1 De omtrek is dan 8 + 4p - 2p2 = 10 |
||||
| 2. | a. | De lengte van het
lijnstuk AB is het verschil tussen beide y-waarden: AB = (p2 – 4p + 6) - (-p2 + 8p – 20) = p2 - 5p + 6 + p2 - 9p + 20 = 2p2 - 14p + 26 De hoogte van driehoek OAB is p De oppervlakte is dan A = 0,5 · p · (2p2 - 14p + 26) = p3 - 7p2 + 13p |
|||
| b. | A' = 3p2
- 14p + 13 = 0 ABC-formule: p = (12 ±√(196 - 156))/6 = 3,05 of 0,94 p = 0,94 geeft A = 6,88 p = 3,05 geeft A = 2,90 Dat laatste is de minimale oppervlakte. |
||||
| c. | Lijnstuk AB heeft
lengte 2p2 - 14p + 26 afgeleide is nul: 4p - 14 = 0 ⇒ p = 3,5 Dat valt dus NIET samen met p = 3,05 |
||||
| 3. | L = f - g
= (4x -
2x2) - (x3 - 4x2
+ 4x) = 4x -
2x2 - x3 + 4x2
- 4x = -x3 + 2x2 L ' = -3x2 + 4x = 0 x(-3x + 4) = 0 x = 0 ∨ x = 4/3 x = 4/3 geeft maximale lengte L = -x3 + 2x2 = 32/27 |
||||
| 4. | x2 - 4x
- 5 = 0 (x - 5)(x + 1) = 0 x = 5 ∨ x = -1 -0,5(x2- 4x - 5) = 0 x2 - 4x - 5 = 0 Dat geeft dan ook x = 5 ∨ x = -1 De parabolen snijden elkaar bij x = -1 en x = 5 op de x-as. Neem aan dat de linkerkant van de rechthoek zich bevindt bij x = p Dan is de afstand tot x = -1 gelijk aan 1 + p De breedte van de rechthoek is dan 6 - 2(1 + p) = 6 - 2 - 2p = 4 - 2p De hoogte van de rechthoek is het verschil van de y-waarden: -0,5(p2 - 4p - 5) - (p2 - 4p - 5) = -0,5p2 + 2p + 2,5 - p2 + 4p + 5 = -1,5p2 + 6p + 7,5 De oppervlakte is dan (-1,5p2 + 6p + 7,5)(4 - 2p) O = -6p2 + 3p3 + 24p - 12p2 + 30 - 15p = 3p3 - 18p2 + 9p + 30 O ' = 9p2 - 36p + 9 = 0 p2 - 4p + 1 = 0 ABC-formule: p = (4 ±√(16 - 4))/2 = 3,73 of 0,27 p = 0,27 is de gezochte waarde, en die geeft O = p3 - 18p2 + 9p + 30 = 31,18 |
||||
| 5. | a. | Als xA
= p dan is AB = 6 - 2p (een parabool is
symmetrisch) De hoogte van de driehoek is dan yA = -p2 + 6p De oppervlakte is dan 0,5(6 - 2p)(-p2 + 6p) = 0,5(-6p2 + 36p + 2p3 - 12p2) = -3p2 + 18p + p3 - 6p2 = -9p2 + 18p + p3 |
|||
| b. | afgeleide is nul:
-18p + 18 + 3p2 = 0 p2 - 6p + 6 = 0 ABC-formule: p = (6 ±√(36 - 24))/2 = 4,73 of 1,27 De juiste waarde is p = 1,27 en dat geeft oppervlakte -9p2 + 18p + p3 = 10,39 |
||||
| 6. | a. | Als xS
= p dan is SQ = 4 - p en RS = 2p2 - 4p
+ 3 De oppervlakte is dan 0,5 • (4 - p)(2p2 - 4p + 3) O = 0,5(8p2 - 16p + 12 - 2p3 + 4p2 - 3p) O = 0,5(-2p3 + 12p2 - 19p + 12) O = -p3 + 6p2 - 9,5p + 6 |
|||
| b. | O ' = -3p2
+ 12p - 9,5 = 0 ABC-formule: p = (-12 ±√(144 - 114))/-6 = 2,91 of 1,09 p = 2,91 geeft de maximale oppervlakte. (dat geeft O = -p3 + 6p2 - 9,5p + 6 = 4,52) |
||||
| 7. | Helling van OP is
yP/xP
= (0,3x3 - 2x2 + 4x)/x
= 0,3x2 - 2x + 4 afgeleide is nul: 0,6x - 2 = 0 x = 2/0,6 = 31/3 Dan is de helling 0,3x2 - 2x + 4 = 2/3 |
||||
| 8. | AB =
(-0,5x2
+ 4) - (-x2
+ 2x + 1) = 0,5x2 - 2x + 3 afgeleide is nul: x - 2 = 0 x = 2 AB = 0,5x2 - 2x + 3 = 1 |
||||
| 9. | a. | verticale afstand is
yf - yg = (
p2
– 4p + 10) - (-2p2 + 18p – 36) =
3p2 - 22p + 46 afgeleide is nul: 6p - 22 = 0 p = 22/6 = 32/3 dan is de afstand 3p2 - 22p + 46 = 52/3 |
|||
| b. | AB = yf - yg
= (
p2
– 4p + 10) - (-2p2 + 18p – 36) =
3p2 - 22p + 46 de hoogte van de driehoek is p de oppervlakte is dan 0,5p( 3p2 - 22p + 46) = 1,5p3 - 11p2 + 23p afgeleide is nul: 4,5p2 - 22p + 23 = 0 ABC-formule: p = (22 ±√(484 - 414))/9 = 3,37 of 1,51 p = 1,51 geeft oppervlakte 1,5p3 - 11p2 + 23p = 14,81 |
||||
| 10. | a. | yQ
= p ⇒ √(1 - xQ) = p ⇒ 1 - xQ = p2 ⇒ xQ = 1 - p2 |
|||
| b. | De oppervlakte is
lengte • breedte. De breedte is xQ - p = 1 - p2 - p De lengte (hoogte) is yQ = p De oppervlakte is dus p(1 - p2 - p) = p - p3 - p2 Dat is maximaal als de afgeleide ervan nul is: 1 - 3p2 - 2p = 0 De ABC-formule geeft dan p = (2 ± √(4 + 12))/-6 = -1 of 2/6 Omdat p > 0 is p = 1/3 de juiste oplossing. |
||||
| 11. | De tweede grafiek
heeft vergelijking y = (x - 2)3 = x3
- 6x2 + 12x - 8 De afstand tussen beide grafieken is dan x3 - (x3 - 6x2 + 12x - 8) = 6x2 - 12x + 8 Dat is minimaal als de afgeleide ervan nul is: 12x -12 = 0 ⇒ x = 1 De afstand is dan 6 • 12 - 12 • 1 + 8 = 2 |
||||
| 12. | De hoogte van de
rechthoek is p2 + 4 De breedte van de rechthoek is 8 - 2p De oppervlakte is dan O =(p2 + 4)(8 - 2p) = -2p3 + 8p2 - 8p + 32 O ' = -6p2 + 16p - 8 = 0 Dat geeft p = 2 ∨ p = 2/3 De oppervlakte is maximaal voor p = 2 en is gelijk aan 32 De oppervlakte is minimaal voor p = 2/3 en is gelijk aan 800/27 maar dat is wel een locaal minimum want voor p = 4 is de oppervlakte gelijk aan nul. |
||||
| 13. |
|
||||
| a
is maximaal als de afgeleide hiervan nul is: a = 3p-1 - p-3 - 1 a '= -3p-2 + 3p-4 = 0 vermenigvuldig alles met p4: -3p2 + 3 = 0 3p2 = 3 p2 = 1 p = 1 (p = -1 voldoet niet) |
|||||
| 14. | a. | f(x)
= 1/(2x - 1) = (2x - 1)-1
f '(x) = -(2x - 1)-2 • 2 = -2/(2x - 1)² In het raakpunt is de helling -2, dus f ' = -2 -2/(2x - 1)² = -2 (2x - 1)2 = 1 2x - 1 = 1 of 2x - 1 = -1 x = 1 of x = 0 maar die laatste vervalt. x = 1 geeft y = 1/(2 • 1 - 1) = 1 dus het raakpunt is (1,1) l is de lijn y = -2x + b en die gaat door (1,1) dus dan is b = 3 l is dus de lijn y = -2x + 3 x = 0 geeft dan y = 3 Het snijpunt van l met de y-as is (0, 3) |
|||
| b. | A is het punt (a, 1/(2a -
1)) Pythagoras tussen O en A: |
||||
|
|
|||||
| Invoeren in de GR en dan calc - minimum geeft (a =
2,20866...) OA = 1,379... De minimale afstand is ongeveer 1,4. |
|||||
| c. | Oppervlakte =
O = 0,5 • a • 1/(2a - 1)=
a/(4a- 2) O ' = (1 • (4a - 2) - a • 4)/(4a - 2)² = - 2/(4a - 2)² De noemer is altijd positief en de teller is altijd negatief. O ' is dus altijd negatief, dus O daalt altijd. |
||||
| 15. | P
= (x, 3/x³) De rechthoek heeft hoogte 3/x³ en breedte x De omtrek is dan O = x + x + 3/x³ + 3/x³ = 2x + 6/x³ Dat is minimaal als de afgeleide ervan nul is O = 2x + 6x-3 O '= 2 - 18x-4 = 0 18x-4 = 2 x-4 = 2/18 = 1/9 x4 = 9 x = 4√9 = 91/4 en dan is y = 3/93/4 P = (91/4 , 3/93/4) |
||||
| 16. | a. | f(x)
- g(x) = (-0,01x3 + 0,20x2
- 1,06x + 6,44) - (-0,01x3
+ 0,16x2 - 0,50x +
1,44) = 0,04x2 - 0,56x + 5,00 Dat is minimaal als de afgeleide ervan nul is: 0,08x - 0,56 = 0 Dat geeft x = 7 |
|||
| b. | h
= (f + g)/2 h = 1/2(-0,01x3 + 0,20x2 - 1,06x + 6,44 - 0,01x3 + 0,16x2 - 0,50x + 0,44) h = -0,01x3 + 0,18x2 - 0,78x + 3,44 |
||||
|
© h.hofstede (h.hofstede@hogeland.nl) |
|||||